Thyroid disease is common in the US – learn more about signs, symptoms
The University of Kentucky Public Relations & Strategic Communications Office provides a weekly health column available for use and reprint by news media. This week's column is by William B. Inabnet III, M.D., UK HealthCare surgeon-in-chief and chair of the Department of Surgery in the UK College of Medicine.
LEXINGTON, Ky. (March 4, 2024) — There are 20 million people in the United States who suffer from thyroid disease. According to the National Cancer Institute, Kentucky has a higher rate of thyroid cancer than the rest of the country.
The thyroid gland is an organ that sits in the neck and controls the body's metabolism. The metabolism processes the food you consume and turns it into energy. Around 50% of the population develops thyroid nodules, yet only 5% of these nodules are malignant.
There are two types of thyroid disease: overactive and underactive. With overactive thyroid disease (hyperthyroidism), there is an excess of the thyroid hormone in the body which leads to the metabolic rate rising. This can lead to panic attacks, anxiety, heat intolerance, hair loss and palpitations of the heart.
The metabolic rate lowers when there is too little thyroid hormone being released (hypothyroidism). Depression, weight gain and thinning of the hair are all symptoms of an underactive thyroid.
Hashimoto's disease versus Graves’ disease. Hashimoto's is the most common thyroid disease, leading to hypothyroidism. Graves’ is more dangerous than Hashimoto’s because of the excess amount of thyroid hormone being pumped into the body can lead to hyperthyroidism.
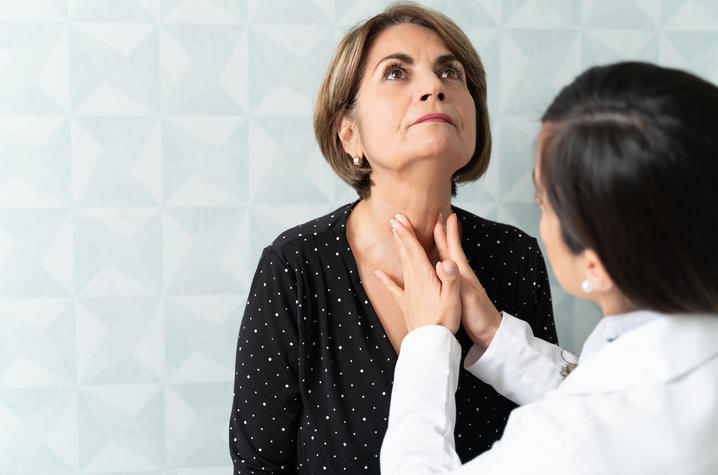
What to look for. To monitor your thyroid health at home, there is a self-examination you can perform called “check the neck.” In this process, you are feeling for a lump, or nodule, on the thyroid gland.
Touch the thyroid gland where it sits over your airway on the neck. If you feel a lump — don’t panic. You can check in with your primary care provider for further care. Typically, an ultrasound is the best way to diagnose thyroid disease or cancer, followed by a biopsy on the nodule.
One of the first ways to check for a problem with your thyroid is to go to your primary care provider and get a blood test. This cannot diagnose thyroid cancer but can check your levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). This blood test can rule out conditions like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
The prognosis of thyroid cancer is very favorable. There is a combination of surgical therapy and other therapies indicated for this cancer.
If you have any questions or concerns, talk to your primary care provider.
UK HealthCare is the hospitals and clinics of the University of Kentucky. But it is so much more. It is more than 10,000 dedicated health care professionals committed to providing advanced subspecialty care for the most critically injured and ill patients from the Commonwealth and beyond. It also is the home of the state’s only National Cancer Institute (NCI)-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center, a Level IV Neonatal Intensive Care Unit that cares for the tiniest and sickest newborns and the region’s only Level 1 trauma center.
As an academic research institution, we are continuously pursuing the next generation of cures, treatments, protocols and policies. Our discoveries have the potential to change what’s medically possible within our lifetimes. Our educators and thought leaders are transforming the health care landscape as our six health professions colleges teach the next generation of doctors, nurses, pharmacists and other health care professionals, spreading the highest standards of care. UK HealthCare is the power of advanced medicine committed to creating a healthier Kentucky, now and for generations to come.




